以下呈現的 序列(Sequence) 主要以 vector 和 array
當然也可以用在 list 、 deque 跟 forward list 喔~~
以下為 print (v) 得程式碼範例
void print(vector<int>tmp){ | |
for(auto i : tmp) | |
cout << " " << i; | |
cout << endl; | |
} |
亦可用代替
void print(vector<int>tmp){ | |
for(int i = 0;i<tmp.size();i++) | |
cout << " " << tmp[i]; | |
cout << endl; | |
} |
# STL 演算法
STL 內部定義了一組專門設計給元素範圍的函式
# 標頭檔
#include<algorithm> |
# 非修改序列演算法 (判斷 / 尋找)
# find
用來尋找指定範圍內,某值的位置。
假設 return 的值是範圍的後一格代表沒有找到其值
#include<algorithm> | |
#include<iostream> | |
#include<vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }; | |
int * p; | |
p = find (myints, myints+4, 30); | |
if (p != myints+4) | |
cout << "Element found in myints: " << *p << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "Element not found in myints\n"; | |
vector<int> myvector (myints,myints+4); | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
it = find (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 30); | |
if (it != myvector.end()) | |
cout << "Element found in myvector: " << *it << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "Element not found in myvector\n"; | |
} |
輸出
Element found is myints: 30
Element found in mycector: 30
# find_if
跟 find 很像,但是其為尋找符合條件值的位置
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool IsOdd (int i) { | |
return (i % 2 == 1); | |
} | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector; | |
myvector.push_back(10); | |
myvector.push_back(25); | |
myvector.push_back(40); | |
myvector.push_back(55); | |
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), IsOdd); | |
cout << "The first odd value is " << *it << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
The first odd value is 25
# count
用於計算範圍內某值出現的次數
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () {: | |
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; // 8 elements | |
int mycount = count (myints, myints+8, 10); | |
cout << "10 appears " << mycount << " times.\n"; | |
vector<int> myvector (myints, myints+8); | |
mycount = count (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 20); | |
cout << "20 appears " << mycount << " times.\n"; | |
} |
輸出
10 appears 3 times.
20 appears 3 times.
以下為 print (v) 得程式碼範例
void print(vector<int>tmp){ | |
for(auto i : tmp) | |
cout << " " << i; | |
cout << endl; | |
} |
亦可用代替
void print(vector<int>tmp){ | |
for(int i = 0;i<tmp.size();i++) | |
cout << " " << tmp[i]; | |
cout << endl; | |
} |
# count_if
用於計算範圍內符合條件的元素數量
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool IsOdd (int i) { return ((i%2)==1); } | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector; | |
for (int i=1; i<10; i++) myvector.push_back(i); | |
// myvector: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
int mycount = count_if (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), IsOdd); | |
cout << "myvector contains " << mycount << " odd values.\n"; | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains 5 odd values. |
# search
用於尋找兩個指定序列完全相同的位置 (首部位置)。
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool mypredicate (int i, int j) {return (i==j);} | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector; | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
// set some values: myvector: 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 | |
for (int i=1; i<10; i++) myvector.push_back(i*10); | |
int needle1[] = {40,50,60,70}; | |
it = search (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), needle1, needle1+4); | |
if (it!=myvector.end()) | |
cout << "the first {40 , 50 , 60 , 70} found at position " << (it-myvector.begin()) << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "{40 , 50 , 60 , 70} not found\n"; | |
// 使用自訂的函式 | |
int needle2[] = {20,30,50}; | |
it = search (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), needle2, needle2+3, mypredicate); | |
if (it!=myvector.end()) | |
cout << "the first {20 , 30 , 50} found at position " << (it-myvector.begin()) << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "{20 , 30 , 50} not found\n"; | |
} |
輸出
the first {40 , 50 , 60 , 70} found at position 3
{20 , 30 , 50} not found
# search_n
尋找連續出現 n 個指定值的那段序列的首位置
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool mypredicate (int i, int j) { | |
return (i==j); | |
} | |
int main () { | |
int myints[]={10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; | |
vector<int> myvector (myints,myints+8); | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
it = search_n (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 2, 30); | |
if (it!=myvector.end()) | |
cout << "{30,30} found at position " << (it-myvector.begin()) << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "match not found\n"; | |
// 自訂比較函式 | |
it = search_n (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 2, 10, mypredicate); | |
if (it!=myvector.end()) | |
cout << "{10,10} found at position " << int(it-myvector.begin()) << '\n'; | |
else | |
cout << "match not found\n"; | |
} |
輸出
{30,30} found at position 2
{10,10} found at position 5
# 修改序列演算法
# copy
就是把 A 複製到 B 上面去
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70}; | |
vector<int> myvector (7); | |
copy ( myints, myints+7, myvector.begin() ); | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
return 0; | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
# swap
就是交換兩個數值或序列用的
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int x=10, y=20; // x:10 y:20 | |
swap(x,y); // x:20 y:10 | |
vector<int> foo (4,x), bar (6,y); // foo:4x20 bar:6x10 | |
swap(foo,bar); // foo:6x10 bar:4x20 | |
cout << "foo contains:"; | |
print(foo); | |
} |
輸出
foo contains: 10 10 10 10 10 10
# transform
讓 A 序列做上一定的變化後到 B 序列上,A 序列不變
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
#include <functional> // std::plus | |
using namespace std; | |
int op_increase (int i) { return ++i; } | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> foo; | |
vector<int> bar; | |
for (int i=1; i<6; i++)foo.push_back (i*10); | |
// foo: 10 20 30 40 50 | |
bar.resize(foo.size()); // 使 bar.size () 一致 | |
transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), op_increase); | |
//foo: 10 20 30 40 50 // bar: 11 21 31 41 51 | |
//plus 功能 能使兩個序列加到另一個上去 | |
transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), foo.begin(), plus<int>()); | |
// foo: 21 41 61 81 101 // bar: 11 21 31 41 51 | |
cout << "foo contains:"; | |
print(foo); | |
cout << "bar contains:"; | |
print(bar); | |
} |
輸出
foo contains: 21 41 61 81 101
bar contains: 11 21 31 41 51
# replace
取代範圍中的 A 全部轉為 B
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = { 10, 20, 30, 30, 20, 10, 10, 20 }; | |
vector<int> myvector (myints, myints+8); | |
// 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20 | |
replace (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 20, 99); | |
// 10 99 30 30 99 10 10 99 | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 10 99 30 30 99 10 10 99
# fill
將指定範圍的所有值都填充為其他值
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector (8); // myvector: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | |
fill (myvector.begin(),myvector.begin()+4,5); // myvector: 5 5 5 5 0 0 0 0 | |
fill (myvector.begin()+3,myvector.end()-2,8); // myvector: 5 5 5 8 8 8 0 0 | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 5 5 5 8 8 8 0 0
# remove
跟 erase() 有一點不同, remove() 只會移除值,並回傳新的 end指標 ,其會停在移除完後序列的後一格位置,移除後的序列大小不變,所以後面會隨機填充。
#include <iostream> | |
#include <vector> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {20,10,20,30,10}; | |
vector<int>myvector(myints,myints+5); | |
vector<int>::iterator vbegin = myvector.begin(); | |
vector<int>::iterator vend = myvector.end(); | |
vend = remove (vbegin, vend, 20); // 10 30 10 ? ? | |
// ^ ^ | |
cout << "range contains:"; | |
for(;vbegin!=vend;vbegin++) | |
cout<<" "<<*vbegin; | |
cout<<endl; | |
} |
輸出
range contains: 10 30 10
# remove_if
跟 remove 一樣,只是條件版本
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool IsOdd (int i) { return ((i%2)==1); } | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
int* pbegin = myints; | |
int* pend = myints + sizeof(myints)/sizeof(int); | |
pend = remove_if (pbegin, pend, IsOdd); // 2 4 6 8 ? ? ? ? ? | |
// ^ ^ | |
cout << "the range contains:"; | |
for (int* p=pbegin; p!=pend; ++p) | |
cout << ' ' << *p; | |
cout << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
the range contains: 2 4 6 8
# reverse
將序列由大到小排列
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector; | |
for (int i=1; i<10; ++i) myvector.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
reverse(myvector.begin(),myvector.end()); // 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 | |
// print out content: | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
# rotate
將序列的前段移動到後段的後面去
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
vector<int> myvector; | |
// set some values: | |
for (int i=1; i<10; ++i) myvector.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
rotate(myvector.begin(),myvector.begin()+3,myvector.end()); | |
// 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 | |
// print out content: | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3
# 排序演算法
# sort
就是一個很常用的排序功能
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool myfunction (int i,int j) { return (i<j); } | |
struct myclass { | |
bool operator() (int i,int j) { return (i<j);} | |
} myobject; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {32,71,12,45,26,80,53,33}; | |
vector<int> myvector (myints, myints+8); // 32 71 12 45 26 80 53 33 | |
// 使用預設比較函式 (operator <): | |
sort (myvector.begin(), myvector.begin()+4); //(12 32 45 71)26 80 53 33 | |
// 使用自訂函式排序 | |
sort (myvector.begin()+4, myvector.end(), myfunction); // 12 32 45 71(26 33 53 80) | |
// 使用物件 operator () 排序 | |
sort (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), myobject); //(12 26 32 33 45 53 71 80) | |
// print out content: | |
cout << "myvector contains:"; | |
print(myvector); | |
} |
輸出
myvector contains: 12 26 32 33 45 53 71 80
# 二分搜演算法
# lower_bound && upper_bound
找出第一個等於或大於特定值的位置
找出第一個大於特定值的位置
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20 | |
sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30 | |
vector<int>::iterator low,up; | |
low= lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ | |
up= upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ | |
cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << '\n'; | |
cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
lower_bound at position 3
upper_bound at position 6
# binary_search
使用二分搜的方法,可以尋找一個值是否出現過,記得需要先排序過
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool myfunction (int i,int j) { return (i<j); } | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+9); // 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 | |
sort (v.begin(), v.end()); | |
cout << "looking for a 3... "; | |
if (binary_search (v.begin(), v.end(), 3)) | |
cout << "found!\n"; else cout << "not found.\n"; | |
sort (v.begin(), v.end(), myfunction); | |
cout << "looking for a 6... "; | |
if (binary_search (v.begin(), v.end(), 6, myfunction)) | |
cout << "found!\n"; else cout << "not found.\n"; | |
} |
輸出
looking for a 3... found!
looking for a 6... not found.
# 合併演算法
# merge
將 A 跟 B 序列結合在 C 序列上
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int first[] = {5,10,15,20,25}; | |
int second[] = {50,40,30,20,10}; | |
vector<int> v(10); | |
sort (first,first+5); | |
sort (second,second+5); | |
merge (first,first+5,second,second+5,v.begin()); | |
cout << "The resulting vector contains:"; | |
print(v); | |
} |
輸出
The resulting vector contains: 5 10 10 15 20 20 25 30 40 50
# 集合 (set) 演算法
總共有四種關係: 聯集、交集、差集以及對稱差
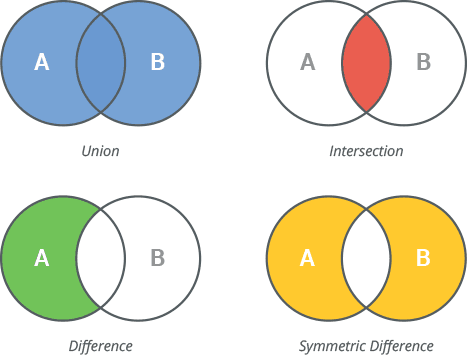
# set_union
將 A 和 B 兩個集合的聯集複製到 C 序列上
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int first[] = {5,10,15,20,25}; | |
int second[] = {50,40,30,20,10}; | |
vector<int> v(10); // 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
sort (first,first+5); // 5 10 15 20 25 | |
sort (second,second+5); // 10 20 30 40 50 | |
it=set_union (first, first+5, second, second+5, v.begin()); | |
// 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 0 0 | |
v.resize(it-v.begin()); // 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 | |
cout << "The union has " << (v.size()) << " elements:\n"; | |
print(v); | |
} |
輸出
The union has 8 elements:
5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50
# set_intersection
將 A 和 B 兩個集合的交集複製到 C 序列上
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int first[] = {5,10,15,20,25}; | |
int second[] = {50,40,30,20,10}; | |
vector<int> v(10); // 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
sort (first,first+5); // 5 10 15 20 25 | |
sort (second,second+5); // 10 20 30 40 50 | |
it=set_intersection (first, first+5, second, second+5, v.begin()); | |
// 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 0 0 | |
v.resize(it-v.begin()); // 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 | |
cout << "The intersection has " << (v.size()) << " elements:\n"; | |
print(v); | |
} |
輸出
The intersection has 2 elements:
10 20
# set_difference
將 A 和 B 兩個集合的差集複製到 C 序列上
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int first[] = {5,10,15,20,25}; | |
int second[] = {50,40,30,20,10}; | |
vector<int> v(10); // 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
sort (first,first+5); // 5 10 15 20 25 | |
sort (second,second+5); // 10 20 30 40 50 | |
it=set_difference (first, first+5, second, second+5, v.begin()); | |
// 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 0 0 | |
v.resize(it-v.begin()); // 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 | |
cout << "The difference has " << (v.size()) << " elements:\n"; | |
print(v); | |
} |
輸出
The difference has 3 elements:
5 15 25
# set_symmetric_difference
將 A 和 B 兩個集合的對稱差複製到 C 序列上
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int first[] = {5,10,15,20,25}; | |
int second[] = {50,40,30,20,10}; | |
vector<int> v(10); // 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | |
vector<int>::iterator it; | |
sort (first,first+5); // 5 10 15 20 25 | |
sort (second,second+5); // 10 20 30 40 50 | |
it=set_symmetric_difference (first, first+5, second, second+5, v.begin()); | |
// 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 0 0 | |
v.resize(it-v.begin()); // 5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 | |
cout << "The symmetric difference has " << (v.size()) << " elements:\n"; | |
print(v); | |
} |
輸出
The symmetric difference has 6 elements:
5 15 25 30 40 50
# 堆演算法
# make_heap
使用 make_heap ,可以使序列的最大值排在最前面
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {10,20,30,5,15}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+5); | |
make_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << '\n'; | |
cout << "vector now contains:"; print(v); | |
} |
輸出
initial max heap : 30
vector now contains: 30 20 10 5 15
# pop_heap
將最大值移動到序列的最尾部,可以再用 pop_back () 刪掉
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {10,20,30,5,15}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+5); | |
make_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << '\n'; | |
pop_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); v.pop_back(); | |
cout << "max heap after pop : " << v.front() << '\n'; | |
cout << "vector now contains:"; print(v); | |
} |
輸出
initial max heap : 30
max heap after pop : 20
vector now contains: 20 15 10 5
# push_heap
將最大值排回到最前面
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {20,15,10,5}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+4); | |
make_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << '\n'; | |
v.push_back(99); push_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout << "max heap after push: " << v.front() << '\n'; | |
cout << "vector now contains:"; print(v); | |
} |
輸出
initial max heap : 20
max heap after push: 99
vector now contains: 99 20 10 5 15
# sort_heap
就是運用建構好的 heap 排序
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <vector> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {99,20,10,5,15}; | |
vector<int> v(myints,myints+5); | |
make_heap (v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout<<"before sorted range : ";print(v); | |
sort_heap(v.begin(),v.end()); | |
cout<<"final sorted range : "; print(v); | |
} |
輸出
before sorted range : 99 20 10 5 15
final sorted range : 5 10 15 20 99
# 最大 / 小值
# min && max
就是求比較小或比較小時用的函式
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
cout << "min(1,2)==" << min(1,2) << '\n'; | |
cout << "max(2,1)==" << max(2,1) << '\n'; | |
cout << "min('a','z')==" << min('a','z') << '\n'; | |
cout << "max(3.14,2.72)==" << max(3.14,2.72) << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
min(1,2)==1
max(2,1)==2
min('a','z')==a
max(3.14,2.72)==3.14
# min_element && max_element
求指定序列的最大值或最小值
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
bool myfn(int i, int j) { return i<j; } | |
struct myclass { | |
bool operator() (int i,int j) { return i<j; } | |
} myobj; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {3,7,2,5,6,4,9}; | |
// 使用預設比較函式: | |
cout << "The smallest element is " << *min_element(myints,myints+7) << '\n'; | |
cout << "The largest element is " << *max_element(myints,myints+7) << '\n'; | |
// 使用自訂函式: | |
cout << "The smallest element is " << *min_element(myints,myints+7,myfn) << '\n'; | |
cout << "The largest element is " << *max_element(myints,myints+7,myfn) << '\n'; | |
// 使用 operator 比較: | |
cout << "The smallest element is " << *min_element(myints,myints+7,myobj) << '\n'; | |
cout << "The largest element is " << *max_element(myints,myints+7,myobj) << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
The smallest element is 2
The largest element is 9
The smallest element is 2
The largest element is 9
The smallest element is 2
The largest element is 9
# 其他
# next_permutation
求當前排列的下一個排列
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {1,2,3}; | |
sort (myints,myints+3); | |
cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n"; | |
do { | |
cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n'; | |
} while ( next_permutation(myints,myints+3) ); | |
cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
After loop: 1 2 3
# prev_permutation
求當前序列的上一個排列
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
int main () { | |
int myints[] = {1,2,3}; | |
sort (myints,myints+3); | |
reverse (myints,myints+3); | |
cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n"; | |
do { | |
cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n'; | |
} while ( prev_permutation(myints,myints+3) ); | |
cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n'; | |
} |
輸出
The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:
3 2 1
3 1 2
2 3 1
2 1 3
1 3 2
1 2 3
After loop: 3 2 1